6 FAQs on Red Spider Mites, or All You Need to Know about Them
A 'red spider mite', as well as a 'two-spotted spider mite', commonly names certain species of pests from the family of about 1,200 spider mites.

Actually, they are lovers of garden plants and trees.
Once their infestation takes place, you will see loads of red spider mites everywhere.
So, why not take a closer look at these insects-arachnids?
Red Spider Mites: 6 Real-World Answers to FAQs
1. What is a red spider mite?
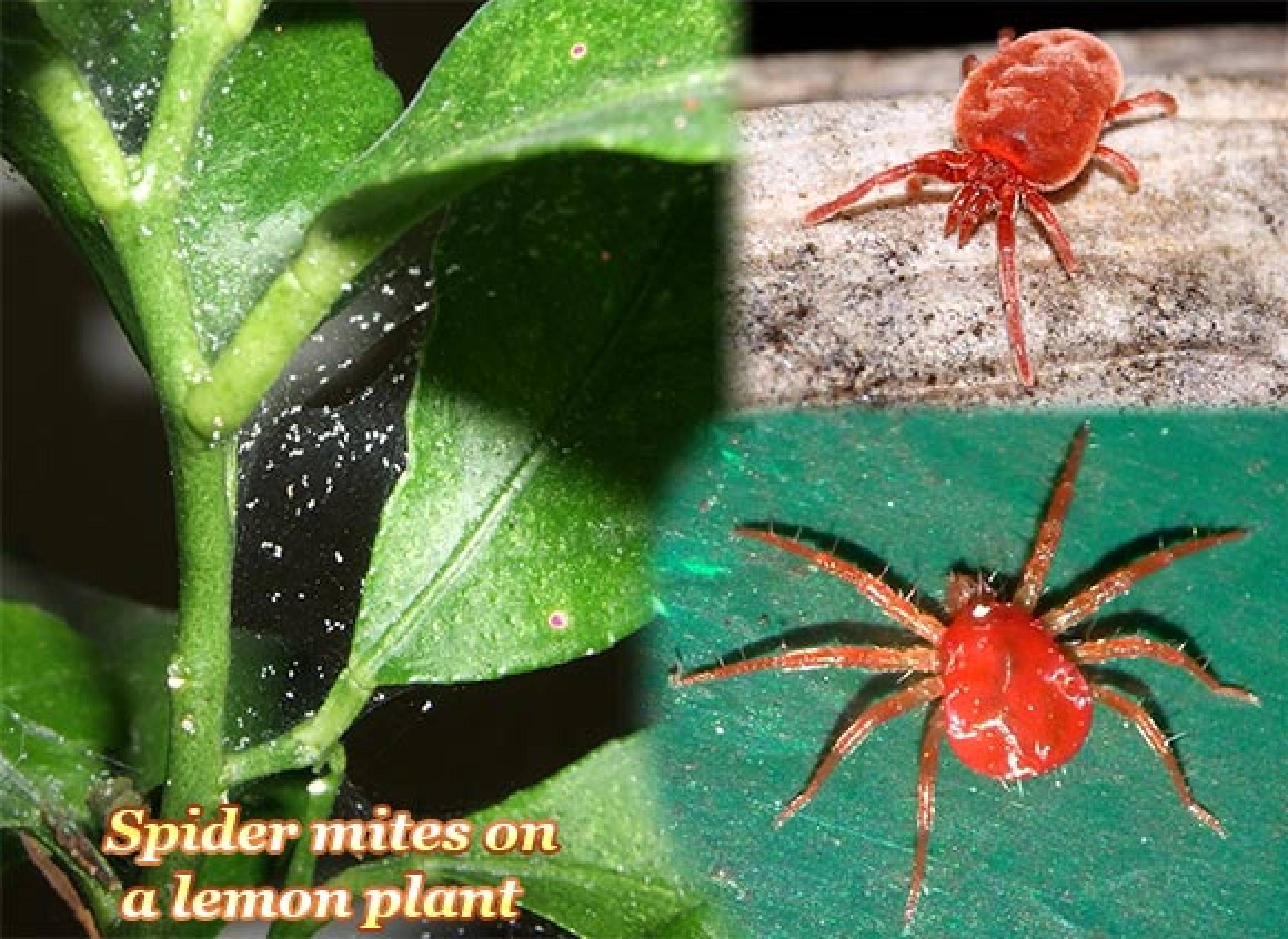
This is an arachnid, but not an insect, though smaller and only with 1 body section (spiders have 2).
Due to the barely visible size, the human eye can notice just reddish or greenish spots on the stems and leaves.
By the way, adults may measure up to 0.4 mm long.
There are European red spider mites (feed on apple trees) and Southern red spider mites (feed on a variety of plants), among which the latter is the most common.
In general, these are crawling and wingless arachnids with 6-8 legs (adults have got 8).
2. What color is a red spider mite?
Most of you would say 'Certainly, red!' Therefore, it is so only at a certain stage, that said after hibernation & in the springtime. Do you know that the newly hatched mite is white, off white or buff-colored? Adults may vary from almost white to green, very dark red or even black.
3. What does a red spider mite eat?
It can feed on most veggies, food crops, and ornamental plants (e.g. roses). The main threat is in that spider mites suck their cell contents.
4. How to identify a red spider mite?
An infested plant will have some webbing and start looking unhealthy on the leaves undersides. Close inspection with a magnifying glass will show that the 'dust' there is moving. Because of the silk webbing, which helps to protect the whole colony from predators, a red spider mite has got the spider part of its common name.
5. What are the most favorable conditions for a red spider mite?
The red spider mite lives in either tropical or temperate zones. Its infestation is most likely to be seen in hot and dry spring, summer and fall. Simply speaking, the heat and dry, dusty atmosphere only speed up the life cycle. On the contrary, a cooler, moist weather slows down their reproductive rate. Optimal conditions for both becoming sexually mature and hatching eggs are 80 °F or 27 °C. A single female can breed a million-population in a month or even less. Amazingly, but adults are able to lay eggs being just 36 hours old!
6. How to control a red spider mite?
The best way of pest control here is with the help of natural predators, including lacewings and ladybugs, along with predatory mites. All of them are available at a good gardening supply center and website. Pesticides can be used too, especially insecticidal soaps & oils that work best. No doubt, No.1 strategy is to make sure you get none of spider mites in the 1st place. Keep your plants and trees healthy and never thirsty! Prevention is always better than any cure.
Ξ Related Post from "Red Spider Mites"